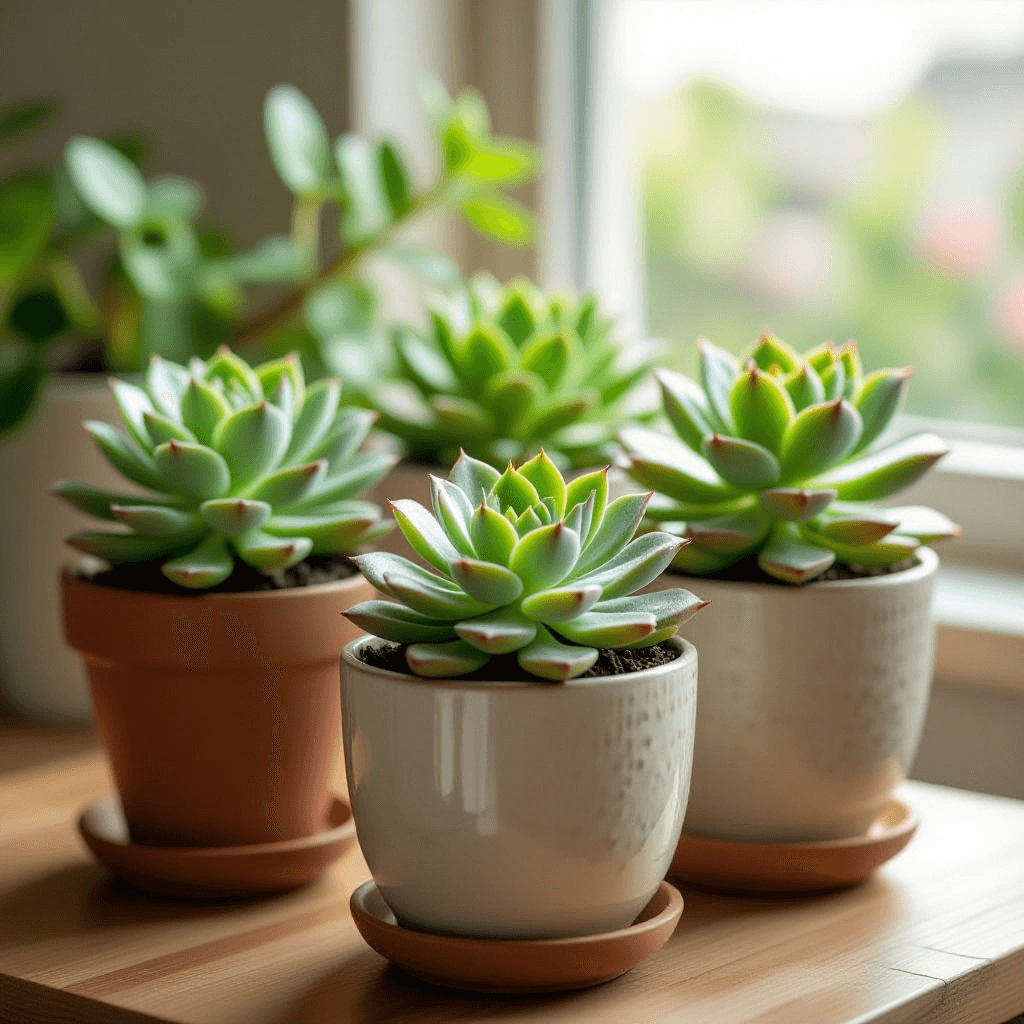
Understanding Succulents: Characteristics and Varieties
Succulents are a diverse group of plants characterized by their unique ability to store water in their leaves, stems, or roots. This water retention allows them to thrive in arid environments where moisture is scarce. One of the most captivating aspects of succulents is their remarkable ability to adapt to harsh conditions, making them popular choices for gardeners and plant enthusiasts around the world. They exhibit various shapes, sizes, and colors, making them an aesthetically pleasing addition to any plant collection.
The term “succulent” describes a wide variety of species, which can be classified into different categories based on their characteristics. Some of the most popular types of succulents include Echeveria, Aloe, and Sedum. Echeverias, known for their rosette formation and vibrant colors, can be found in shades ranging from deep purple to powdery blue. Aloes, including the well-known Aloe Vera, are not only recognized for their decorative appeal but also for their medicinal properties. Sedums, often called stonecrops, are particularly hardy plants that can thrive in extreme conditions, making them ideal for outdoor rock gardens or containers.
When considering succulent care, it is vital to understand that each variety may have specific light, temperature, and humidity requirements. For example, while some succulents prefer bright, indirect sunlight, others can tolerate direct exposure. Similarly, temperature preferences can vary; some may thrive in cooler conditions, while others flourish in warm environments. Moreover, humidity levels play a critical role in succulent health, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot and other diseases. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these unique characteristics and varieties, plant owners can provide appropriate care tailored to each succulent type, ensuring they remain vibrant and healthy.
Essential Care Tips for Thriving Succulents
Caring for succulents requires a fundamental understanding of their unique needs. One of the most crucial aspects of succulent care is managing water. Succulents are adapted to dry climates, meaning they store water in their leaves and stems. As a general rule, it is essential to allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings. Overwatering is one of the most common mistakes that succulent owners make, leading to root rot—a condition that can jeopardize the plant’s health. A simple approach is to water deeply but infrequently, only when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch.
Another critical factor in succulent care is light exposure. Different varieties of succulents have varying light requirements, ranging from bright indirect light to direct sunlight. Placing succulents in a location that receives ample sunlight is vital for their growth. For example, haworthias and gasterias thrive in low light, while echeverias and sedums require bright light to maintain their vibrant colors and compact forms. Observing your plants for signs of stress—such as elongated leaves or color fading—can help inform you whether to move them to a brighter or shadier spot.
The choice of soil and pot also significantly impacts the health of your succulents. A well-draining soil mix designed explicitly for cacti and succulents is ideal, as it allows excess water to escape quickly, preventing waterlogged roots. Additionally, pots with drainage holes are essential for ensuring proper drainage. Common mistakes include using regular potting soil or containers without drainage holes, both of which can lead to complications in the plant’s health.
By focusing on these key elements—appropriate watering practices, light conditions, and soil selection—succulent owners can create an optimal environment that promotes healthy growth and longevity for their plants.
Common Pests and Diseases: Prevention and Treatment
Succulents, while resilient, are susceptible to various pests and diseases that can impede their growth and overall health. Common pests include mealybugs, aphids, and spider mites. Mealybugs, often appearing as small, cotton-like clusters, can typically be found on the undersides of leaves or in leaf joints. These pests suck sap from the plant, leading to weakness and stunted growth. Aphids, which are soft-bodied insects that vary in color, can also be found on new growth, inflicting similar damage. Spider mites, though microscopic, create webs and cause yellowing leaves, making early detection crucial.
In addition to pests, succulents may suffer from various diseases like root rot, primarily caused by overwatering and poor drainage. This condition manifests as yellowing, wilting leaves, and a foul smell from the soil. Early identification of these issues is key to preserving the health of your succulents. Regular inspection of your plants will help spot signs of infestation or disease promptly.
Preventative measures play a significant role in maintaining succulent health. Utilizing well-draining soil and ensuring proper pot drainage can prevent root rot. It is also essential to maintain hygiene by cleaning the pots and tools used for succulent care to mitigate the risk of introducing pests or pathogens. Additionally, consider placing your succulents in an area with good air circulation and appropriate light for optimal growth.
When dealing with pests, natural remedies such as neem oil and insecticidal soap can effectively eliminate infestations without harming the plant. If the problem persists despite treatment, consulting a professional may be necessary to explore further solutions. Thus, understanding the common pests and diseases, along with their prevention and treatment, is vital for keeping your succulents thriving.
Propagation Techniques: Growing Your Succulent Collection
Propagation is an effective way to expand your succulent collection without significant financial investment. Understanding the various propagation techniques can empower you to grow new plants from your existing ones. The most common methods include leaf propagation, stem propagation, division, and offsets. Each technique has unique steps and requirements, ensuring a successful outcome when performed correctly.
Leaf propagation involves carefully selecting a healthy leaf from the parent plant. Using a sterile cutting tool, detach the leaf from the stem, ensuring it remains intact without any tears. Allow the leaf to callous over for a few days in a dry location, which diminishes the risk of rot. Once the leaf has formed a callous, place it on moist, well-draining soil, preferably a succulent mix, and ensure it receives indirect sunlight. Over time, tiny roots and new plantlets will emerge at the base of the leaf.
Stem propagation, on the other hand, requires cutting a stem section from the parent plant. Similar to leaf propagation, ensure the cutting tool is sterile for optimal results. The cut section should then be allowed to dry and callous for several days. Once prepared, place the stem in well-draining soil and provide adequate light. New growth should appear within weeks, indicating successful propagation.
Another method is division, typically used for succulents that grow in clusters. Gently separate the offsets or baby plants from the parent clump, ensuring each one has a healthy root system. After separating them, allow the wounds to dry before planting in their designated pots with suitable soil. Finally, offsets are small baby plants that grow directly from the base of the mother plant. These can often be pulled away with minimal damage, planted, and allowed to root.
For all propagation techniques, ensure you monitor moisture levels and provide proper lighting. Positioning new plants in conditions that mimic their parent plants will significantly enhance their chances of thriving. By mastering these propagation methods, succulent enthusiasts can effectively grow their collections and share their love for these resilient plants.