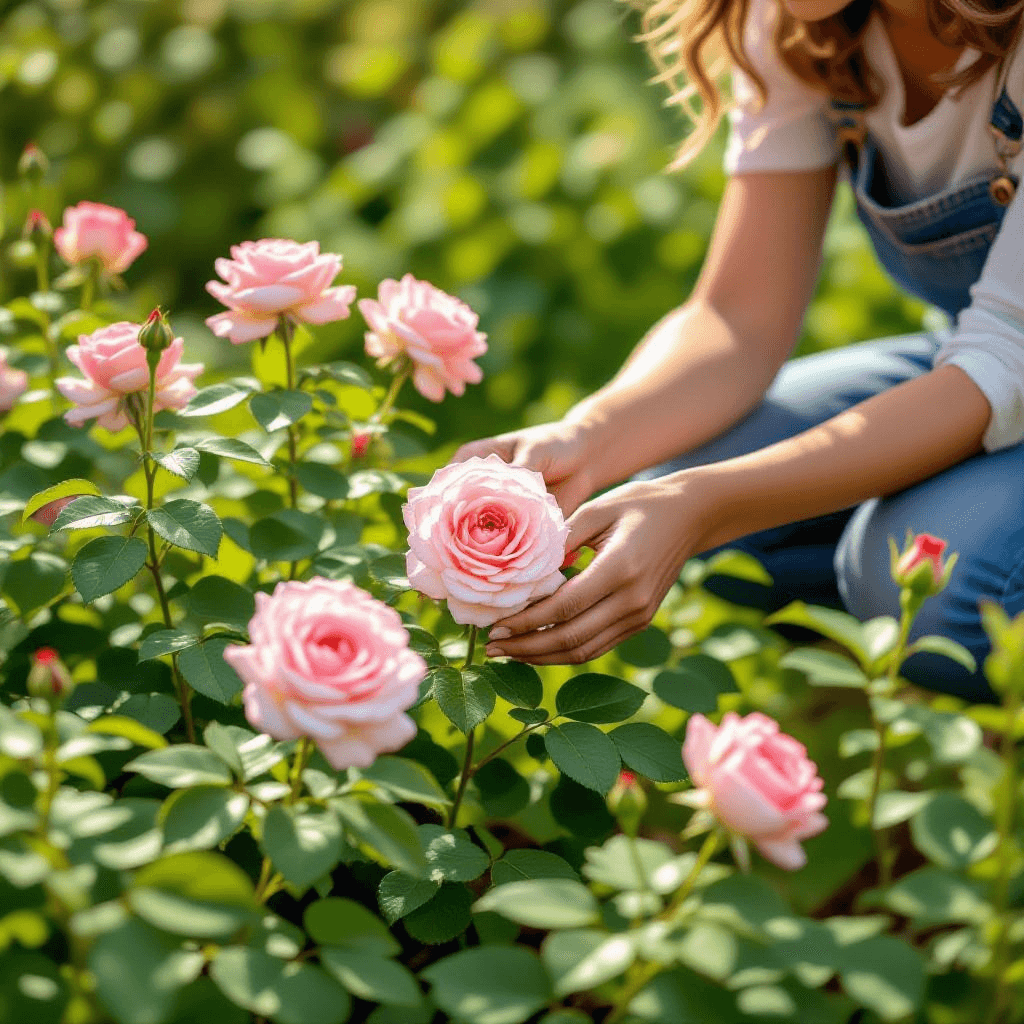
Choosing the Right Rose Varieties
When embarking on the journey of growing roses, selecting the appropriate rose varieties is paramount, particularly for novice gardeners. There are several types of roses that are suitable for beginners, including hybrid teas, floribundas, and climbing roses, each catering to different gardening preferences and environments. Understanding the characteristics of these varieties is essential in making an informed choice.
Hybrid teas are renowned for their classic, elegant blooms and high-quality flowers. These roses often produce large single blooms on long stems, making them ideal for cut flower arrangements. They thrive in well-drained soil and require full sun, making them a great choice for gardeners who are committed to providing regular upkeep. Floribundas, on the other hand, are known for their abundant clusters of smaller flowers that provide a prolonged display throughout the growing season. Their hardiness and disease resistance make them particularly appealing to beginner gardeners looking for a vibrant addition to their landscape.
Climbing roses also deserve consideration, especially for those with limited garden space or a desire to create vertical interest. These varieties can be trained to grow on trellises, fences, or walls, providing a beautiful framework in any garden. While all rose types require optimal care, choosing those that are adaptable to your local climate is essential to ensuring their successful growth.
Moreover, understanding your gardening goals—be it for stunning aesthetics, delightful fragrance, or long-lasting durability—will also inform your choice of roses. It’s advisable to consult local nurseries or trustworthy online suppliers to find reputable sources of rose varieties. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific environment, further enhancing your chances of cultivating a flourishing rose garden. Selecting the right rose varieties will set a solid foundation for your gardening endeavors.
Preparing Your Garden for Roses
Proper preparation is crucial when establishing a vibrant rose garden. The first step involves conducting a thorough soil test to gauge nutrient levels and pH. Roses thrive best in soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8. If your soil test indicates higher alkalinity or acidity, you can amend the soil accordingly. Adding organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure can enhance soil structure and nutrient content, fostering a healthier environment for your roses.
Drainage is another vital aspect to consider. Roses do not flourish in overly saturated soil, which can lead to root rot. Ensure that your garden bed has proper drainage by incorporating light materials such as sand or perlite to sandy soils. For clay-heavy areas, consider raised beds to improve drainage and aeration. A well-drained garden bed creates an ideal habitat for roses, allowing for healthy root development and preventing diseases.
Sunlight is essential for the robust growth of roses. Ideally, select a planting site that receives at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. Observe current garden features and neighboring plants to identify optimal locations for your rose bushes, as well as ensuring adequate spacing. Providing sufficient space between your plants promotes air circulation, reducing the risk of fungal diseases and enhancing growth potential.
Furthermore, selecting the right tools and materials contributes to creating a rose-friendly environment. Essential tools include a spade for digging, a rake for smoothing soil, and a watering can or hose for consistent moisture. Investing in high-quality organic fertilizers will further support your roses’ growth. By taking these preparatory steps and considering the surrounding environment, novice gardeners can set the foundation for a thriving rose garden.
Care and Maintenance of Roses
To cultivate healthy and vibrant rose plants, understanding their care and maintenance is crucial. Watering is the foundation of rose care. Roses require deep watering, ideally once a week, ensuring the soil is moist but not soggy. Drip irrigation is recommended as it provides water directly to the roots, reducing the likelihood of fungal diseases. During hot summer months, roses may need additional watering, so monitoring soil moisture is essential.
Fertilization also plays a significant role in rose plant health. Using a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for roses can promote robust growth and abundant blooms. Apply fertilizer in early spring as new growth begins, followed by additional applications every six weeks throughout the growing season. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid over-fertilization, which can lead to nutrient burn.
Pruning helps maintain the shape and size of rose plants while encouraging new growth and flowering. The ideal time for pruning is in late winter or early spring before new buds start to emerge. Remove dead or diseased wood and cut back 1/3 of the previous year’s growth to stimulate healthy development. Observing your roses for signs of diseases, such as black spot or powdery mildew, is vital. Implementing good air circulation and keeping foliage dry can minimize disease occurrence.
Pest control is another critical consideration in rose care. Common pests such as aphids and spider mites can harm your plants. Regularly inspecting your roses for these pests and applying insecticidal soap or natural predators can help keep infestations at bay. Seasonal tasks also include preparing your roses for winter. Mulching around the base and covering the plants with burlap can protect them from the cold. Conversely, as spring approaches, early pruning promotes fresh blooms, while ensuring proper ventilation prevents fungal outbreaks.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Rose Gardening
Rose gardening can be a rewarding yet challenging pursuit, particularly for beginners. As roses are susceptible to a range of environmental factors, pests, and nutrient deficiencies, understanding how to troubleshoot these common issues is essential for maintaining healthy plants. One of the first steps in addressing problems in rose gardening is to identify the specific symptoms exhibited by the plants.
Pests such as aphids, spider mites, and thrips can significantly damage rose bushes. These insects often congregate on new growth, causing leaves to curl or discolor. Regular inspection of your roses can help you catch infestations early. Natural solutions include introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs or using insecticidal soap, which effectively targets pests without harming the plants. Furthermore, properly maintaining soil health can strengthen rose plants, making them less susceptible to pest damage.
Nutrient deficiencies can also affect rose health, manifesting as yellowing leaves or stunted growth. Common deficiencies in rose plants include nitrogen, potassium, and magnesium. To address this, it is advisable to use a well-balanced fertilizer, specifically formulated for roses, or to conduct soil tests to better understand which nutrients might be lacking. Additionally, mulching can improve soil quality and retain moisture, aiding in overall plant vitality.
Furthermore, environmental factors such as excessive heat, poor drainage, or insufficient sunlight can hinder the growth of roses. Ensuring that roses are planted in appropriate conditions—with adequate sunlight and proper air circulation—will improve their resilience. Moreover, using organic amendments can enhance soil drainage and nutrition, thereby creating a more conducive environment for rose growth.
For additional support, consider engaging with online forums and local gardening clubs, where enthusiasts share tips and solutions tailored to specific issues in rose gardening. These resources can provide invaluable insights and foster connections with experienced gardeners who can offer assistance.